Codes and Conventions
- zainfaridr
- Apr 8, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: May 12, 2025
Narrative Structure and Postmodern Elements: The film opening integrates key postmodern elements that subvert linear storytelling in favour of emotional truth and internal subjectivity. Through a fragmented narrative, the story is revealed via present-day action and stylised flashbacks. These flashbacks are constructed with a stop-motion effect at 3 to 4 frames per second, combined with halation, motion blur, and glow, producing a visual distortion that reflects trauma and nostalgia. Rather than offering a literal replay of memory, these sequences feel emotionally fragmented, placing the audience inside the protagonist's disoriented mind.

The rejection of classical structure and equilibrium situates the film within a postmodern framework. It begins in emotional unrest, avoids exposition-heavy dialogue, and instead relies on mise-en-scene, atmosphere, and performance to gradually construct meaning. This invites the audience to engage interpretively. The use of Barthes enigma code is central to this approach. Questions are raised early on through visuals and subtext, with no immediate answers provided, deepening suspense and thematic ambiguity. Genre hybridity also plays a role, as the film mixes naturalistic settings with heightened cinematography, resulting in an aesthetic that reinforces the psychological tension at its core.
Flashback Sequence as a Psychological Code:
The flashback sequence in the film was designed not as a traditional memory but as a stylised reflection of a traumatic experience. The stop-motion visual treatment, operating at only a few frames per second, paired with glowing highlights and motion blur, creates a dreamlike unreality. These effects establish a nostalgic yet disorienting atmosphere, aligning with the thematic codes of psychological thrillers where memory is often unreliable and fragmented. This distorted visual form functions as a subtextual representation of the protagonist’s mental state.
Costume and Dress Codes:
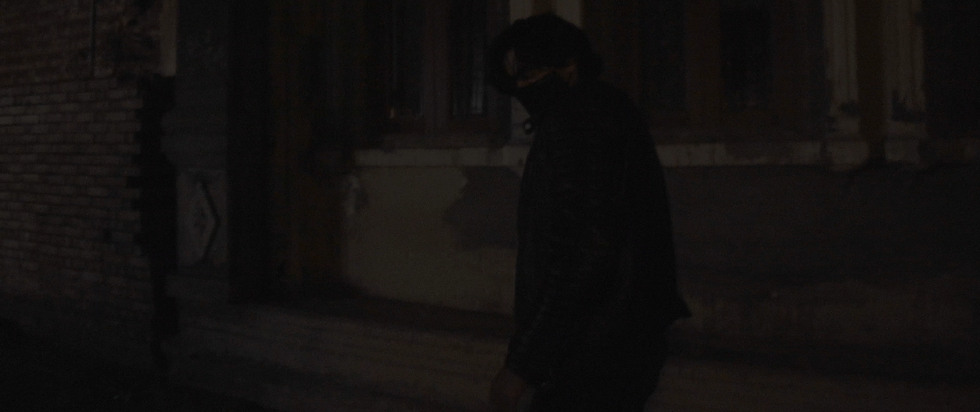
Dress codes in the film directly reflect character motives and tone. Raahim is shown wearing a black hoodie, black cargo trousers, and a mask. This costume choice visually codes anonymity, suppressed identity, and underlying intent. It aligns with genre expectations where antagonistic figures in psychological thrillers often dress to obscure themselves. In contrast, the indoor apartment scenes feature casual clothing that reflects the domestic realism of the environment and situates the audience in a familiar yet uneasy space. The shift between threatening attire and domestic wear supports the film's duality between internal and external conflict.


Sound Design and Music Codes:
The soundscape of the film was composed using layered synth pads and sampled instrumentals. E major synths appear in emotionally heightened moments, creating warmth or tension depending on the scene. During tense or investigative sequences, fast-paced ambient instrumentals underscore a sense of urgency. All sound design was custom-created to support psychological immersion, aiding tone modulation and enhancing atmosphere. These auditory codes are consistent with genre expectations, where sound is used to trigger subconscious emotional responses in the viewer.
Camera Work and Technical Codes: Camera techniques were selected based on both aesthetic and narrative logic. One continuous take was used during the stakeout scene to simulate the realism of a live recording, reinforcing the idea that Saif’s brother is capturing their first mission. Close-up shots were deployed to express emotional subtlety and allow the viewer to study micro-expressions. Wide shots provided spatial context, reinforcing the psychological isolation of the characters within a realistic environment. The 180-degree rule and shot reverse shot editing were maintained during conversations to preserve spatial orientation. Low-angle and high-angle shots were also used strategically to convey shifting power dynamics and vulnerability.
180* Rule
Shot Reverse Shot. Ignore the focus on the first shot, manual focus pulling in a moving shot is not 100% effective.
Location and Setting as Psychological Symbolism: All locations were deliberately selected to echo the codes of psychological thrillers. Rather than extravagant or stylised settings, the film uses domestic spaces such as apartments and rooftops to root the narrative in realism. This realism intensifies the unease, as it places unsettling emotions within recognisable environments. Locations were not only functional but symbolic, reflecting the duality of personal and public personas. The confined apartment space acts as a metaphor for emotional entrapment and internal claustrophobia.

Lighting and Visual Tone: Lighting was controlled to maintain both naturalistic and cinematic qualities. During interior scenes, practical lighting was combined with diffused key lights to create shadows and uneven exposure. This design mimics emotional instability and aligns with the atmospheric needs of a psychological thriller. Cooler tones were used in tense scenes to elicit discomfort, while warmer lighting was reserved for moments of emotional openness. This shift in lighting direction plays a subliminal role in influencing viewer perception of character intent and emotional vulnerability.
Colour Scheme and Symbolic Palette: The film follows a green and orange colour scheme, traditionally used to represent tension, unease, and emotional contradiction. Green evokes sickness, emotional decay, or false security, while orange reflects warmth and proximity. By using these complementary colours, the film introduces both comfort and suspicion into the frame. This duality supports the film’s psychological undertone, suggesting internal conflict beneath seemingly calm surfaces.


Editing and Genre-Specific Techniques:
The editing rhythm mirrors psychological fluctuation. Long takes build realism and immersion, while sharp cuts in flashbacks or emotionally charged moments disrupt that flow to reflect instability. Techniques such as vignette framing, glowing edges, and overlay effects were selectively used to add tension and surrealism. These stylistic decisions draw from psychological thriller conventions, where editing reflects mental fragmentation and sensory overload. All visual effects were chosen to reinforce the audience’s alignment with the protagonist’s psyche.
Mise-en-Scene and Visual Composition: Every element within the frame was curated with symbolic intention. Set design was minimal and functional, allowing emotional tension to dominate rather than visual clutter. Objects such as helmets, bags, and everyday appliances were arranged with realism but also coded significance, pointing toward routine, pressure, or unspoken history. Blocking and actor positioning within frames reflected distance or intimacy, depending on the emotional weight of the scene. The mise-en-scene operates not only as background but as an emotional map of the characters psychological states.














Comments